Seals Help Researchers Discover New Seawater Pathways in Antarctica
Researchers have uncovered new seawater pathways in Antarctica with the help of seals equipped with sensors. These seals provided critical data about ocean temperature, salinity, and currents.
The discovery has significant implications for understanding how melting ice shelves interact and affect global sea levels.
Warm Water's Role in Melting Ice Shelves
Warm water flowing underneath ice shelves accelerates their melting, contributing to rising sea levels. This process doesn’t occur in isolation. Ocean currents distribute the meltwater around the Antarctic coast, impacting downstream ice shelves.

Source: henrique setim/Unsplash
Understanding these currents is helps to predict future sea level changes.
The Bellingshausen Sea: A Crucial Region
The Bellingshausen Sea, located near South America, is the first point where warm Atlantic and Pacific waters reach the ice shelves.

Source: NASA/Michael Studinger/Wikimedia Commons
This region has been understudied, but recent research has highlighted its importance. As the warm water melts the ice shelves, it cools and becomes fresher, altering its melting capacity.
Interconnected Ice Shelves
Ice shelves in Antarctica are interconnected systems. Melting in one area can influence processes in another, creating a domino effect.

Source: Cassie Matias/Unsplash
To predict changes accurately, researchers must understand how these systems interact. “What happens in one ice shelf changes the processes at another,” says Caltech’s Andy Thompson.
Advanced Research Techniques
Researchers have used advanced techniques to study these processes. Underwater autonomous vehicles and sensor-equipped seals have been instrumental in gathering data.
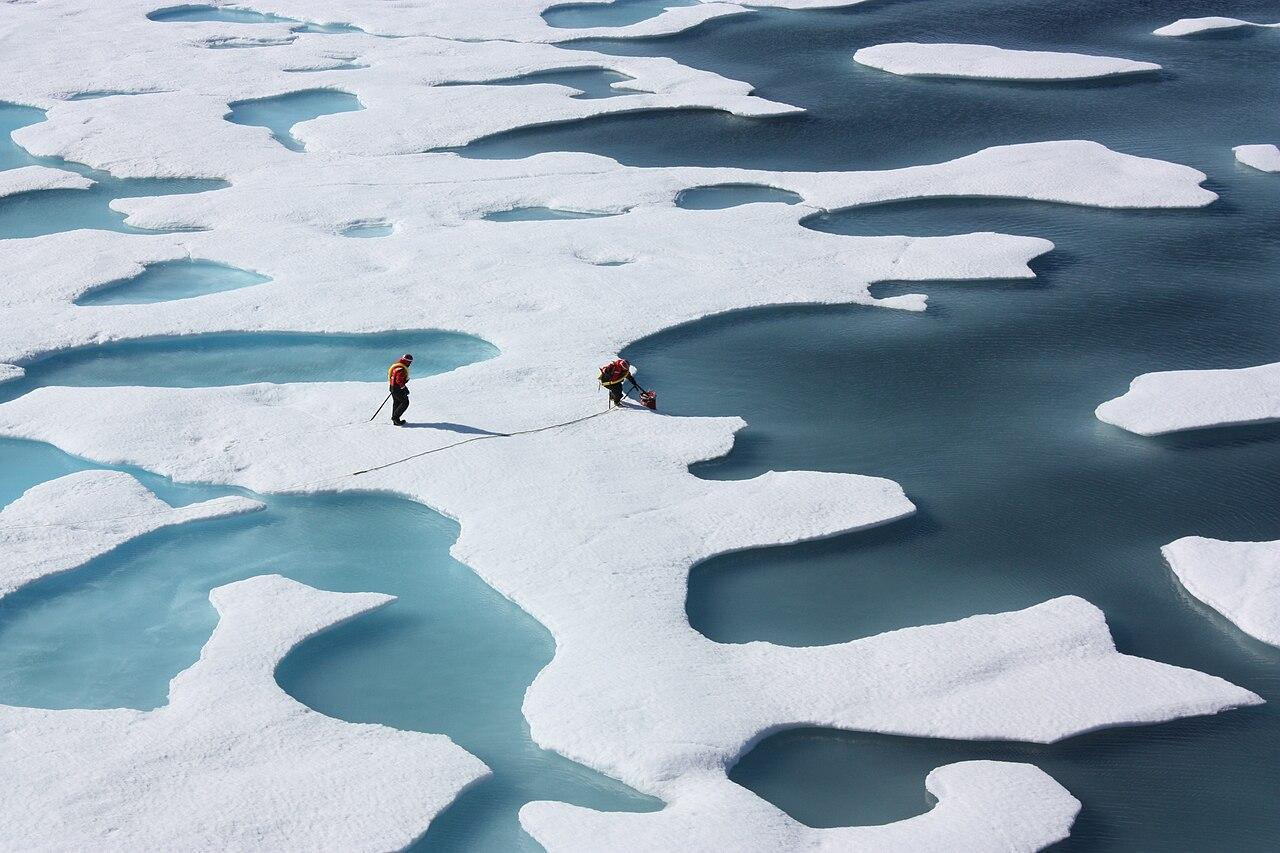

Source: Wikimedia
This combination has provided a comprehensive view of the Antarctic seas, revealing previously unknown currents and underwater features.
The Role of Marine Mammals
Seals play a vital role in this research. As part of the Marine Mammals Exploring the Oceans Pole to Pole (MEOP) program, seals are equipped with small sensors that measure various oceanic properties.
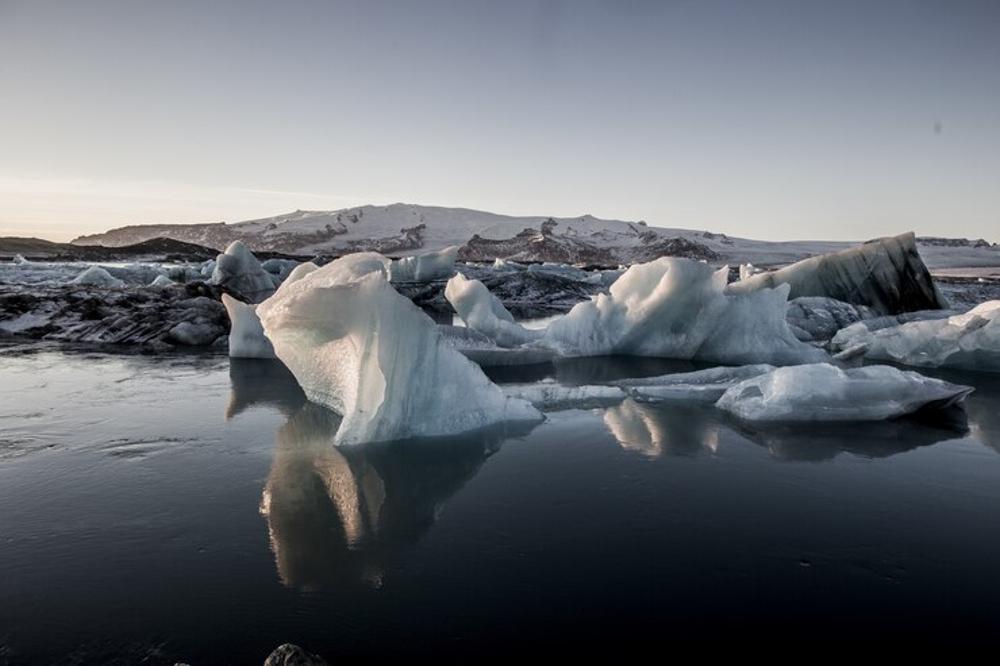

Source: Freepik
This collaboration has been ongoing for decades, providing valuable data to researchers worldwide.
Discovering the Seal Trough
The data collected by seals led to the discovery of a previously unknown underwater trough, now named Seal Trough.
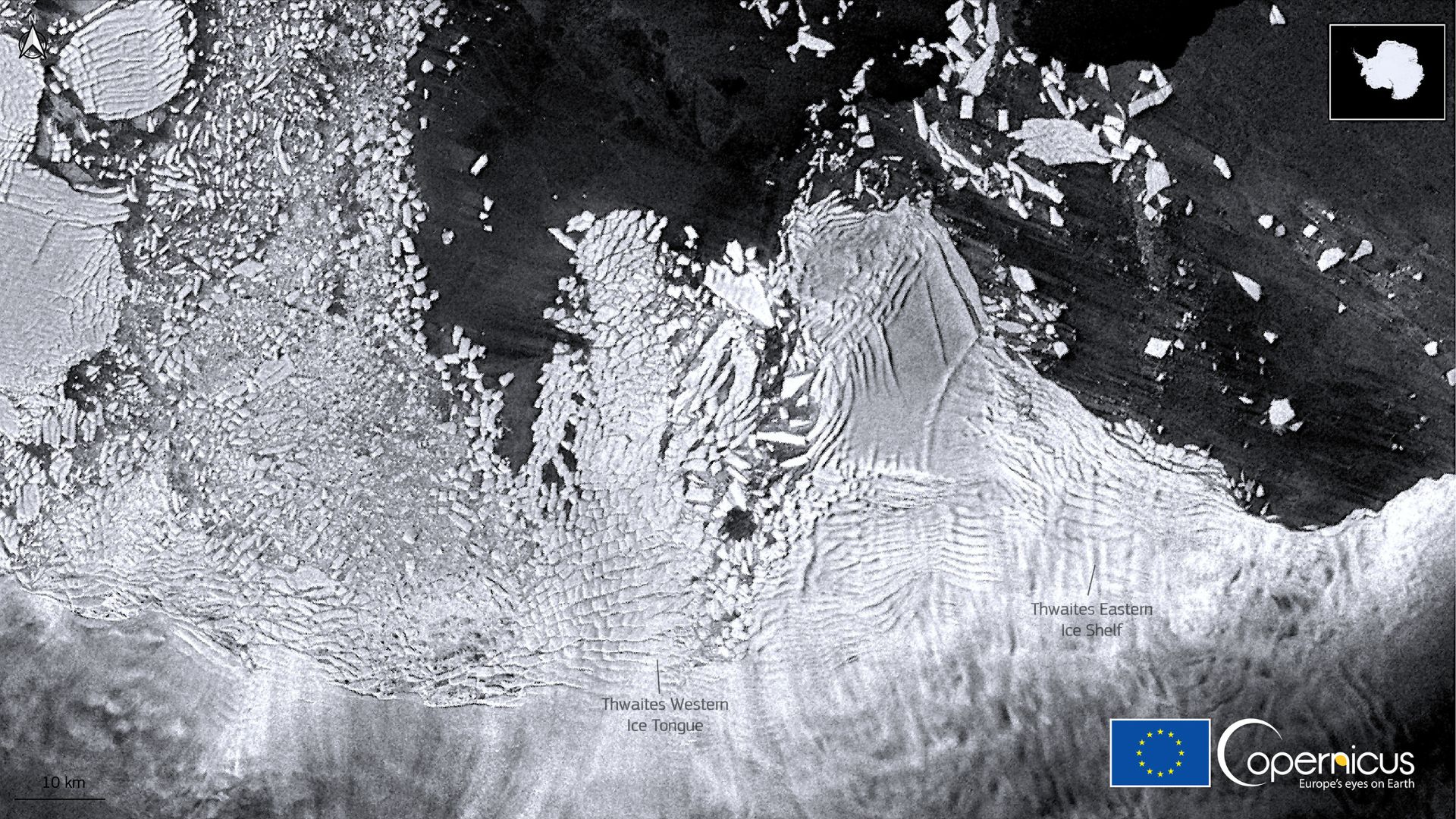
Source: Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data 2021/Wikimedia Commons
This feature influences the flow of currents, similar to how canyons on land guide rivers. Understanding such features is crucial for mapping meltwater pathways.
Mapping Meltwater Pathways
Researchers identified two distinct meltwater pathways originating from different ice shelves.

Source: Asile Clairette/Unsplash
One pathway follows the coast, trapping warm waters at depth and increasing melting at downstream ice shelves. The other pathway returns to the open ocean, carrying cooler, fresher water away.
Predicting Future Sea Level Rise
This research is a major step in understanding how individual ice shelves influence larger Antarctic circulation.

Source: Wikimedia
As the oceans continue to warm, improved knowledge of these processes is essential to predict future rates of global sea level rise accurately.
International Collaboration
The study is a result of international collaboration, involving researchers from several institutions.

Source: Cytonn Photography/Pexels
This cooperation has been vital in collecting and analyzing data, highlighting the importance of global teamwork in addressing climate change.
Funding and Support
The research received funding from prestigious organizations such as the National Science Foundation, NASA, and the European Research Council.

Source: David McNew/Getty Images
These grants support the ongoing study of Antarctic ice shelves and their impact on global sea levels.
Looking Ahead
As climate change continues to impact the planet, understanding Antarctic ice melt is more important than ever.

Source: Torsten Dederichs/Unsplash
Continued research and international collaboration will be crucial in developing strategies to mitigate and adapt to rising sea levels.
